Virtual Private Network, or VPN in short, is one of the most commonly used features on our security gateways, and with Nebula, you can configure VPN on your USG FLEX in a few minutes!
Synopsis
This article will cover all common VPN scenarios, be it Remote access VPN or Site-to-Site VPN (including VPN to non-Nebula peers). To access the configuration options, please, log into Nebula Control Center using your credentials at https://nebula.zyxel.com/ and navigate to the following menu depending on the type of VPN you want to create:
USG FLEX > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN
USG FLEX > Configure > Remote access VPN
Table of Contents
- Remote Access VPN: L2TP over IPSec
- Remote Access VPN: IPSec client
- Site-to-Site VPN: Nebula peers
- Site-to-Site VPN: non-Nebula peers
- Site-to-Site VPN: VPN Orchestrator and advanced configurations
Remote Access VPN: L2TP over IPSec
To configure L2TP over IPSec VPN, please navigate to the Remote access VPN menu and enable L2TP over IPSec VPN option. The only mandatory fields to make your VPN working are to fill in your secret (Preshared Key) and Client VPN subnet. You only need to consider using a subnet that is not yet used anywhere else. You may want to change the DNS servers or set the authentication to a local server, for example, but this is completely optional. The "Default" button next to Policy opens a menu that allows you to set IPSec proposals. The default values are designed to be compatible with most operating systems.
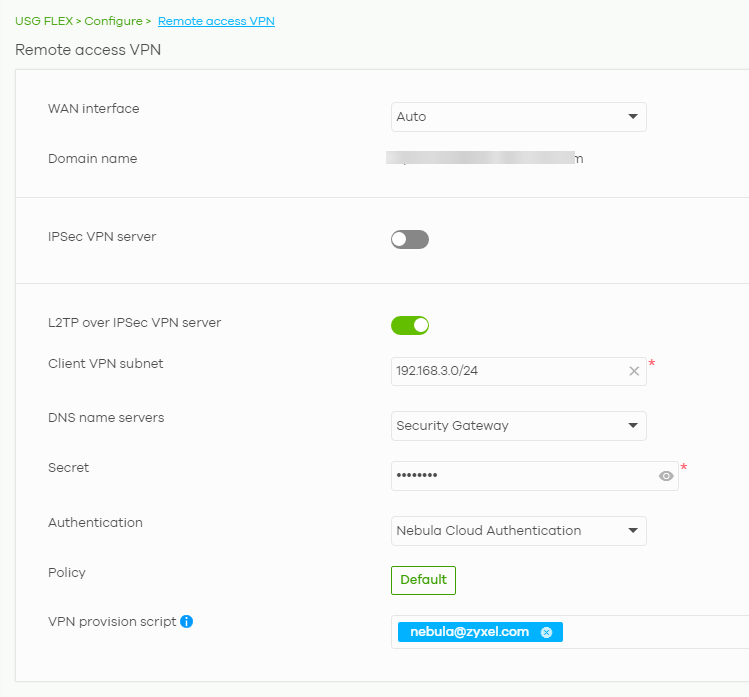
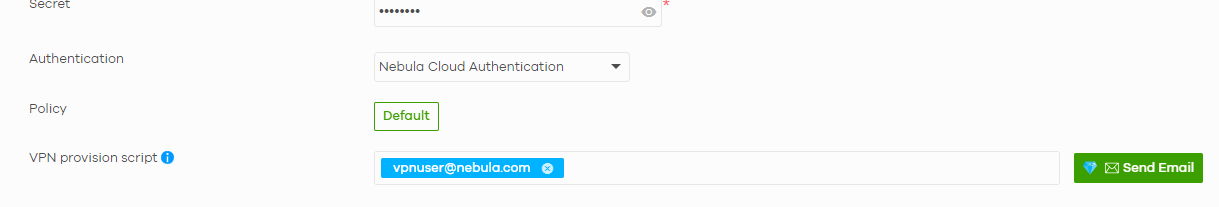
After you save your configuration, you may take advantage of the VPN provision script feature - fill in a list of recipients and click the "Send Mail" button. The configuration script with instructions on how to use it will be sent to the provided addresses.
Client configuration - Provision script mode
Nebula Pro offers a convenient way to configure Windows or macOS clients using a VPN provisioning script. This can be sent directly to users:
Once the mail is sent, users will receive a mail from info@nebula.zyxel.com that contains the provisioning scripts: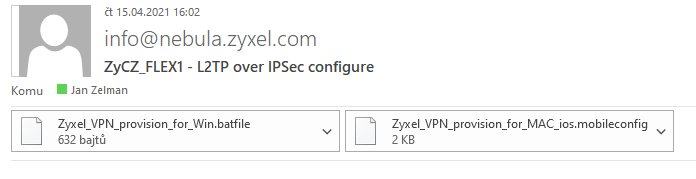
As their name suggests, the .batfile file is intended for Windows, while the .mobileconfig file is intended for macOS. Due to security restrictions, the .batfile file needs to be renamed to .bat before execution. Simply double-clicking the script will create a VPN connection on your system. During the first connection, the user needs to provide his credentials. These will be saved after the first successful connection.
Client configuration - Manual mode
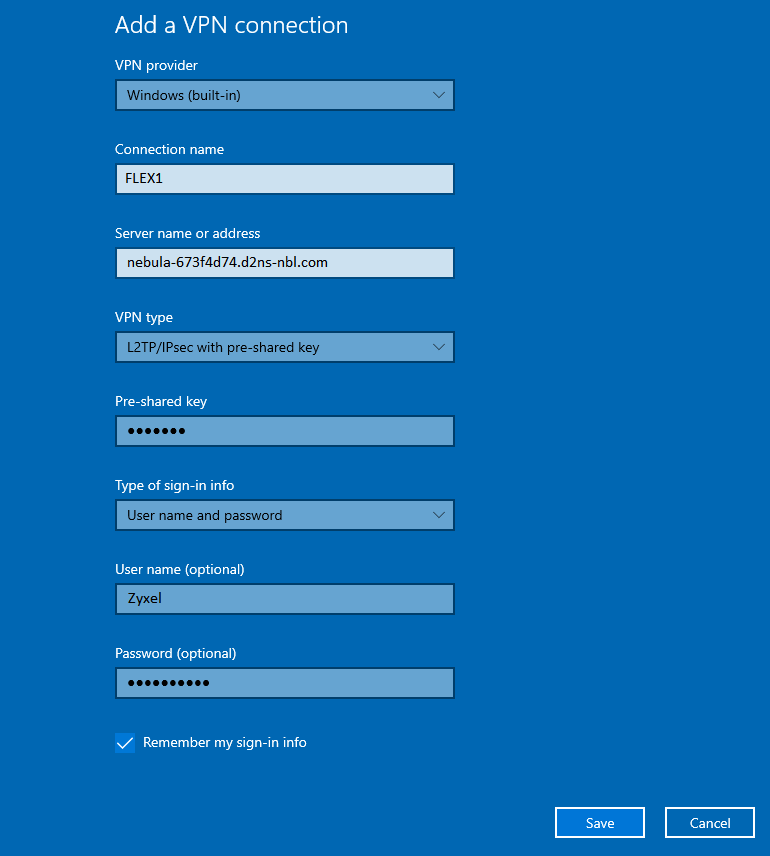
It is, however, no hard task to configure the VPN manually. On Windows, please navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > VPN and click on Add VPN Connection.
Fill in the form according to the credentials provided by Nebula (You may use either IP address or DDNS automatically generated by Nebula), and you're all set!
Remote Access VPN: IPSec client
In a similar fashion to L2TP over IPSec configuration, the IPSec VPN configuration also takes place in the Remote Access VPN menu and starts with the IPSec VPN server checkbox. The only mandatory fields to make your VPN working are to fill in a secret (Preshared Key) and Client VPN subnet. The only thing to consider is to use a subnet that is not yet used anywhere else. You may want to change the DNS servers or set authentication to a local server, for example, but this is optional. The "Default" button next to Policy opens a menu that allows you to set IPSec proposals. The default values are designed to provide high security to your IPSec connections. You may also enable two-factor authentication for your clients to enhance security even further by Google authenticator.
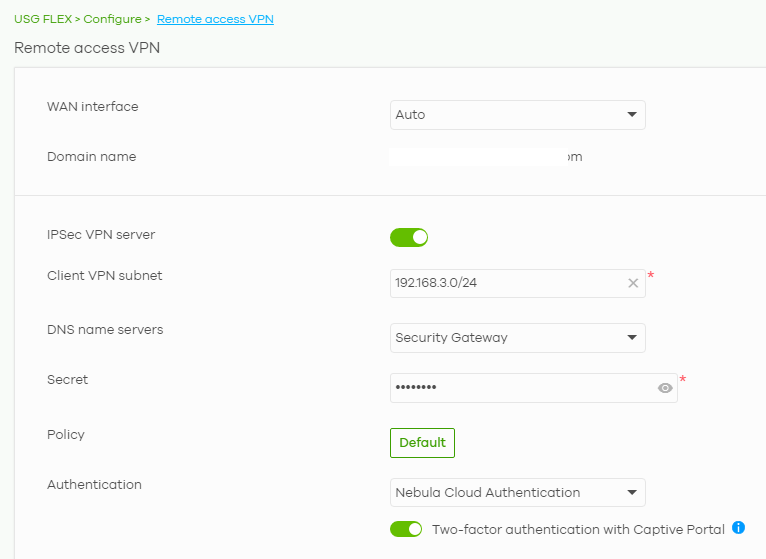
Client configuration
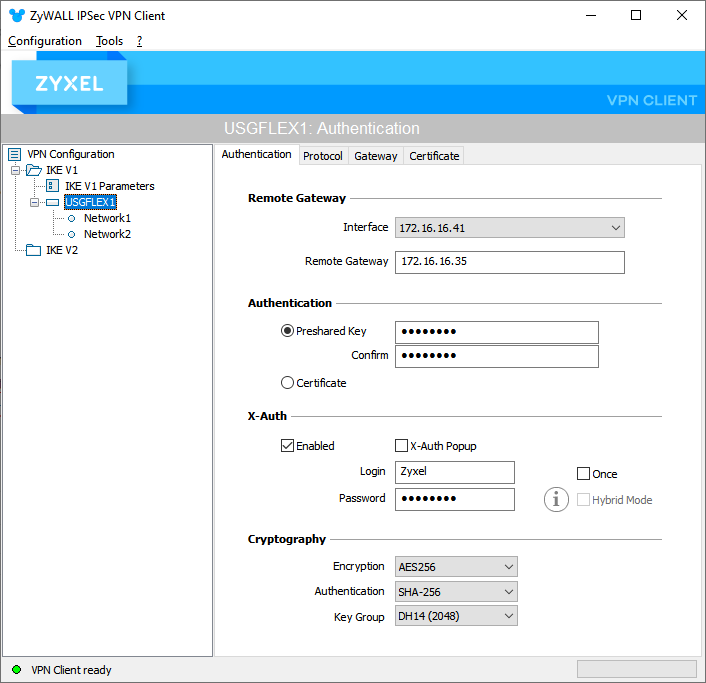
Configuring the client is very simple. First, we want to create the IPSec Gateway and fill in the details on the Authentication tab, such as in the following example, which considers default cryptography values:
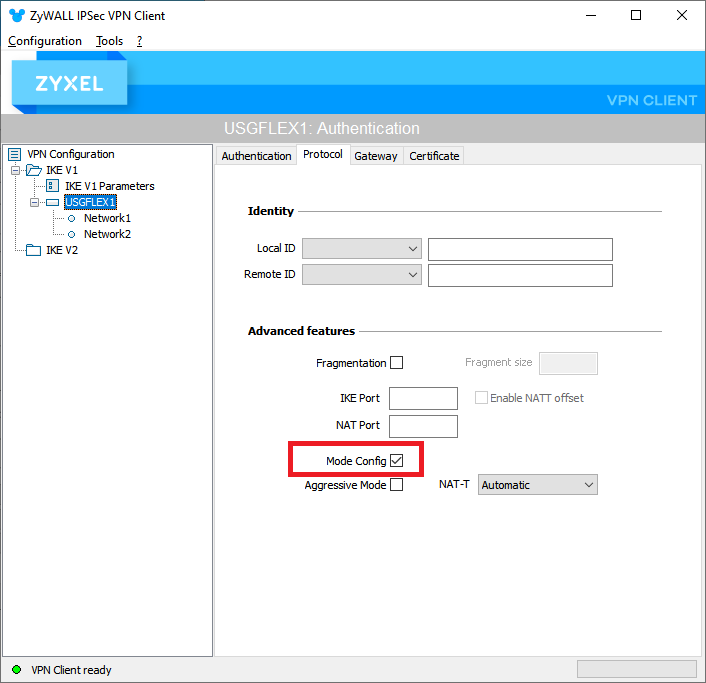
On the Protocol tab, it is important to select the "Mode Config" box:
Now we are ready to create an IPSec connection. Please fill in the target network address, ESP/PFS parameters and you are ready to connect. You may also create multiple networks and access them simultaneously:
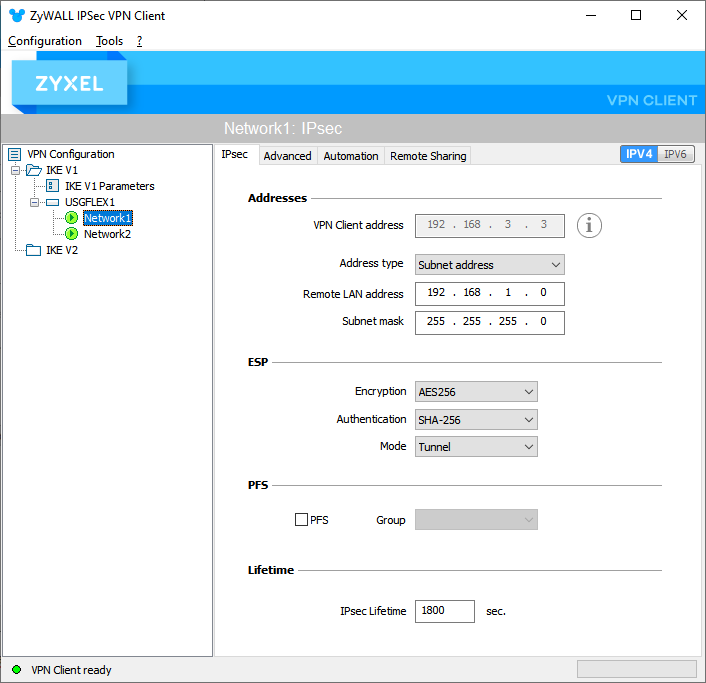
That's it! Now you are ready to connect remotely. Remember that the IPSec client can always export the configuration once it is finished to deploy it on multiple devices easily.
Site-to-Site VPN: Nebula peers
Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN has never been easier. The Site-to-Site VPN menu starts with WAN interface configuration. You may choose a single WAN interface as outgoing or leave the option as auto to provide redundancy. In that case, you will be asked which interface should be preferred.
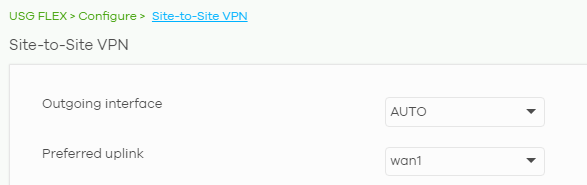
The configuration then continues to your local networks, where local interfaces and remote VPN connections are available to participate in the site-to-site VPN connection.

In the next section, you may configure the advanced settings. For example, you may select the desired VPN Area for your network - smaller networks will be fine with just one Default VPN area. Larger or simply more elaborate VPN structures may need to use more VPN Areas. More information regarding the VPN Area and Nebula VPN Orchestrator can be found in the last chapter.
The NAT traversal option allows you to customize your WAN IP address for your VPN. This is useful in situations where multiple IPs are routed to your WAN port and you want to use a specific address for VPN.
Site-to-Site VPN: non-Nebula peers
Adding a non-Nebula peer naturally requires a configuration on the Nebula Control Center and the standalone device.
On the Nebula side, it is only required to fill in some information about the connection, notably the name that will identify the device, its public IP address, and a remote private subnet that you intend to connect to the preshared key. Optionally, you may edit the IPSec policy to suit your needs and set which sites will access this router. Please note that the private subnet property should not be a network address but should be an actual device address used for connection check purposes in CIDR format - for example, the remote VPN server itself.

Important:
Special characters like -, +, ^, *, [, ], \, ", ? are not allowed.
This will change in the future.
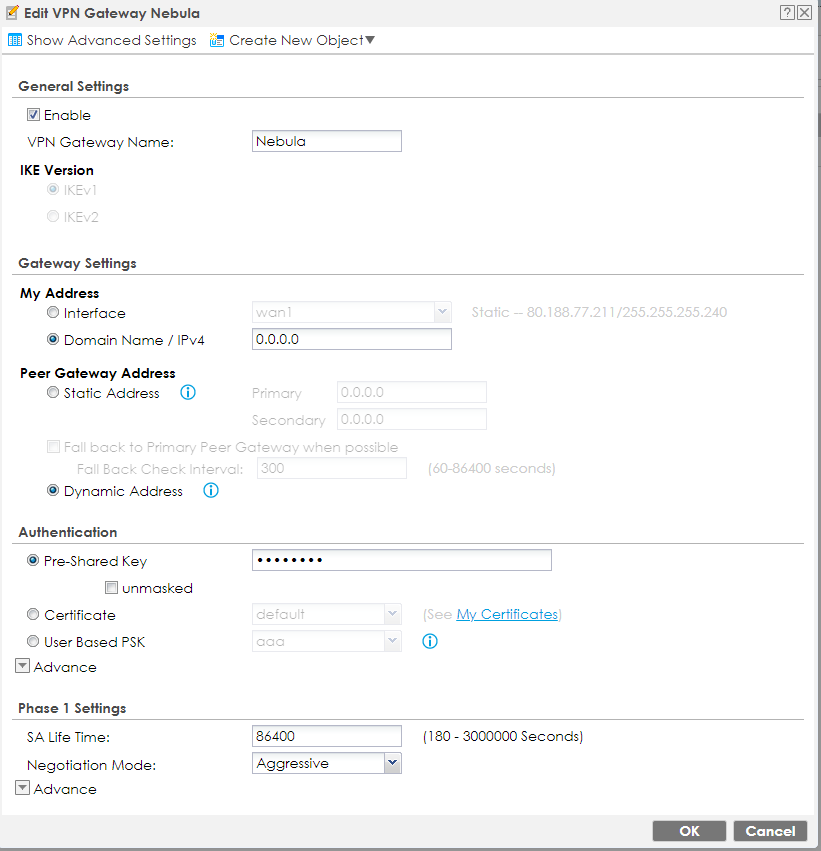
In this case, on the side of the remote router, ATP200, we will need to create a VPN gateway first. Following configuration will allow you to reuse this gateway for as many peers as you wish. With the default IPSec proposal, only change the negotiation mode to "Aggressive" and pre-shared key is necessary.
After the configuration of the VPN Gateway, the VPN connection will finally allow us to establish the connection between the two routers. Please set the local and remote policy according to your network topology. These values must match the configuration in Nebula. Otherwise, the negotiation will fail.
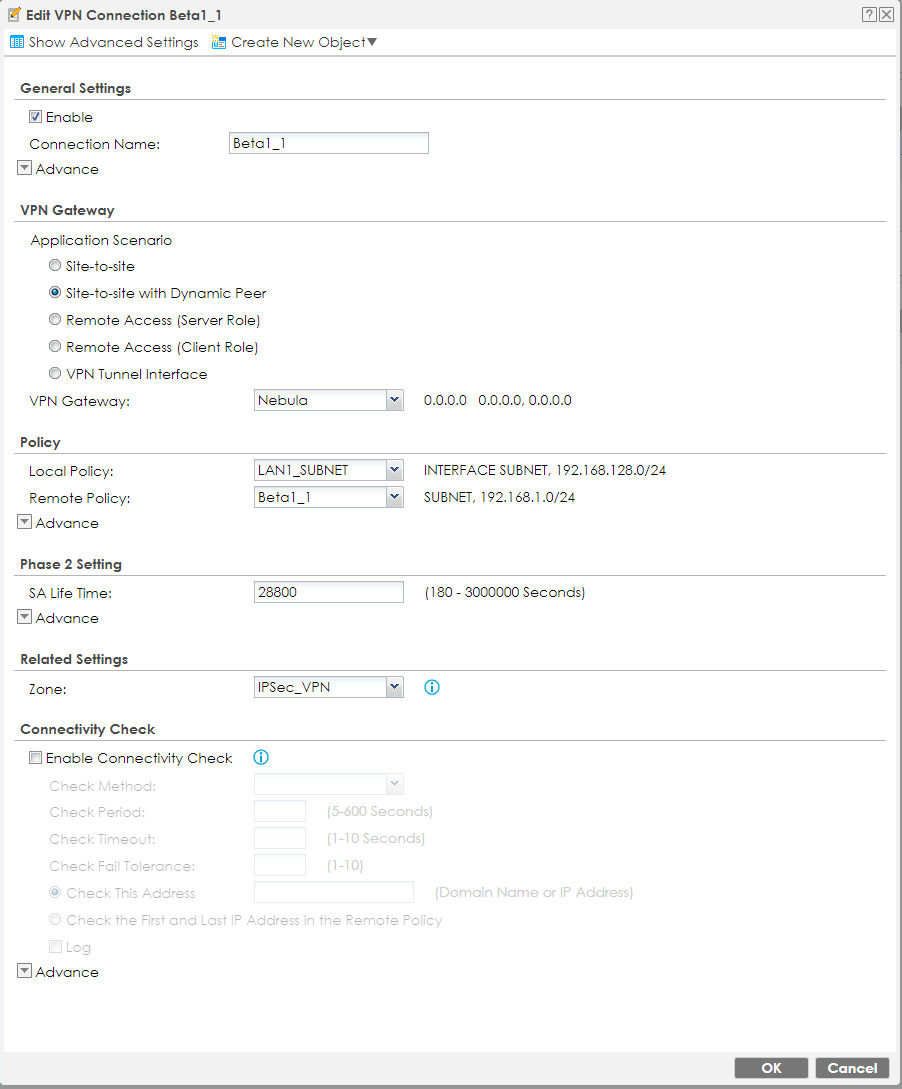
After saving the VPN connection, the connection between the routers should be established within few seconds.

Site-to-Site VPN: VPN Orchestrator and advanced configurations
The Nebula VPN Orchestrator is a powerful tool that allows you to configure complex VPN topologies with ease. The NCC platform allows for abstract configuration without configuring individual VPN connections on each gateway and seamlessly changing the topology based on your current requirements with just a few clicks!
Nebula VPN topology explained
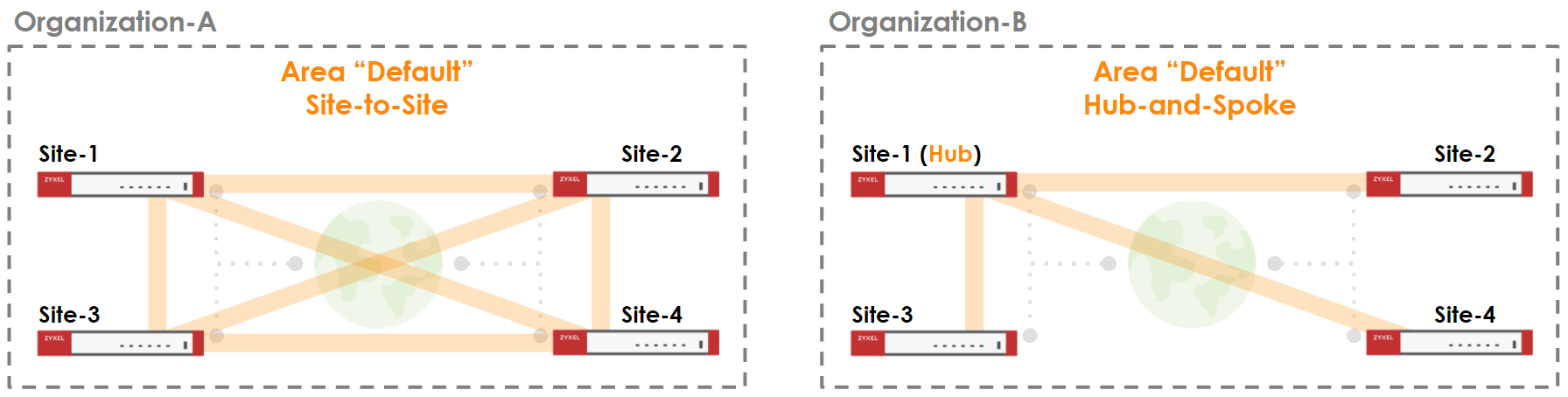
Nebula Orchestrator can contain multiple VPN Areas. Each area can be either Site-to-Site topology or Hub-and-Spoke topology. In Site-to-Site topologies, every security gateway connects to all other gateways within the VPN area. In Hub-and-Spoke topologies, the only gateway designated as Hub will connect to other gateways. It is also possible to have one or more Site-to-Site areas and other Hub-and-Spoke areas.
Each area can have up to five Hubs unless the area contains an NSG - in that case, only a single Hub be in a given area. If the Hub has its outgoing interface set to "auto", all WAN connections will dial the VPN connections to the Spoke gateways simultaneously.
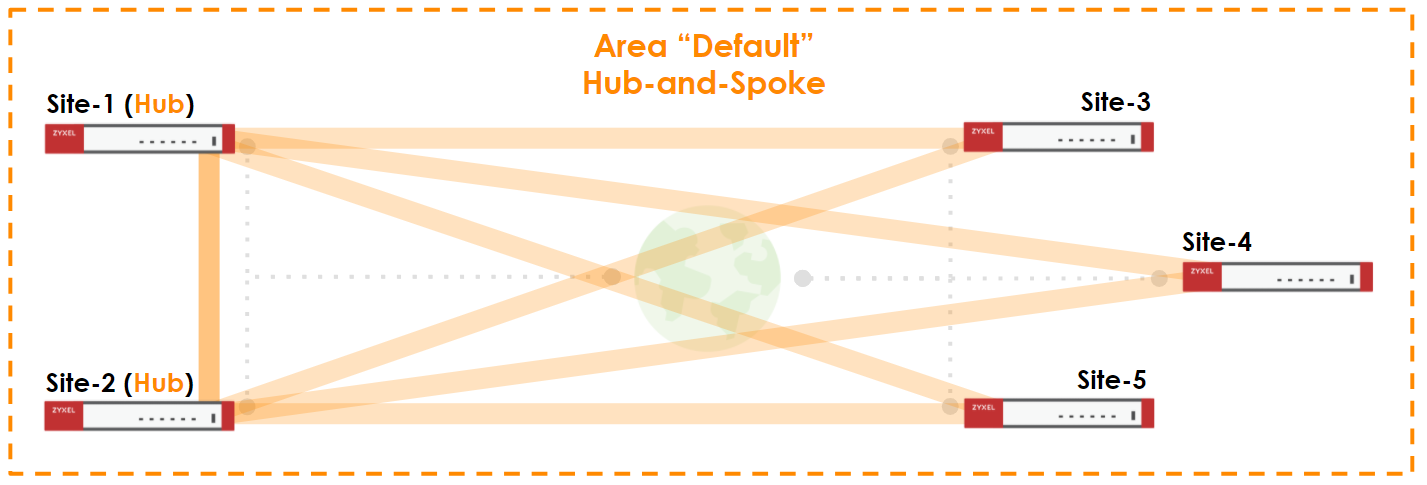
To communicate between areas, you can enable Area Communication for the gateway. Site-to-Site areas need to have a designated Area Leader for this to work. The Area Leaders or Hub gateways will dial VPN tunnels to other areas and allow a communication between the AC gateways.
Configuration
The VPN Orchestrator configuration can be found in the following menu:
Organization-wide > VPN Orchestrator
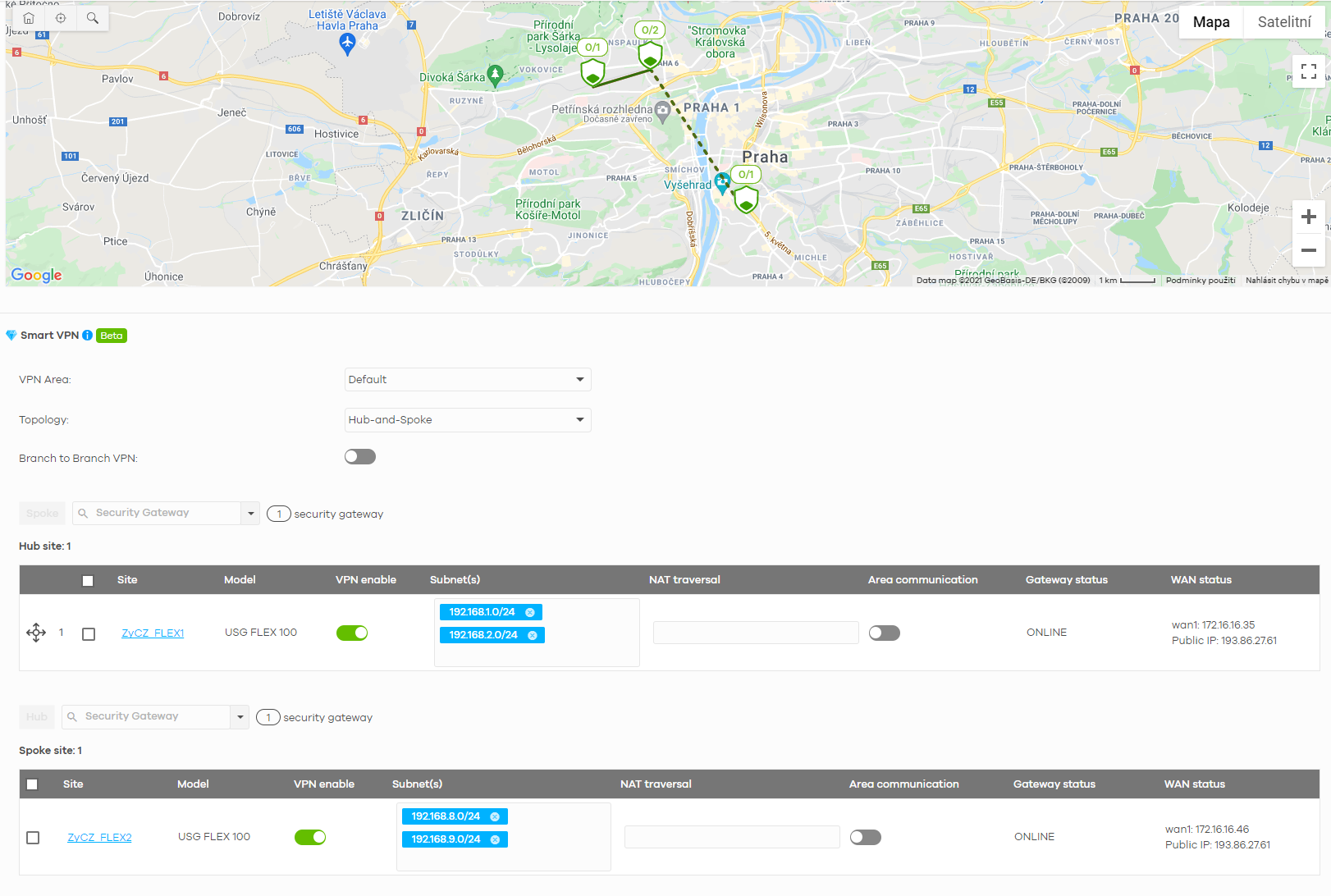
The top part of the screen shows a map with a current visualisation of the VPN network - including faults due to loss of connection. This also includes non-nebula peer connections - these can be distinguished with a dashed line.
In the Smart VPN menu, you may select the desired area you wish to configure or create a new one and select the desired topology.
Based on your selection, you may need to designate Hubs and Spokes in the same menu. But in any case, you will be able to select which gateways will connect to the VPN, which subnets on these gateways will participate in the VPN connections and configure the Area Communication status of the device.
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.