Overview
This guide is designed to help with the first time Wi-Fi setup on the P660HN. This walkthrough will guide you through the process of setting up a wireless network name (SSID) and strong wireless security profile (WPA2). Recommendations to acquire the best possible performance will also be given in the tweaks section. Please be aware that wireless performance will depend on environmental variables and hardware capability.
Accessing the Web Configurator
To access the device web configuration screen to configure the wireless settings, please connect your computer directly to an available LAN port. A wired computer is needed to minimize downtime for the Wi-Fi configuration. During the configuration process wireless devices will lose connection to the network, this is why it is not recommended to make any configuration changes via wireless.
Open an internet browser (Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, etc.) and delete the contents of the address bar. Type http://192.168.1.1 on the address bar and hit the enter/return key on the keyboard. 192.168.1.1 is the ZyXEL default IP address, if your ZyXEL modem/router was provided to you by the internet service provider it may be running proprietary firmware/software based on your provider's standards for operation. If this is the case you may need to contact the service provider to obtain the IP address for the web configurator and login credentials (administrative credentials). Once the correct web configurator address is entered on the browser, the following screen will appear requesting the administrator credentials.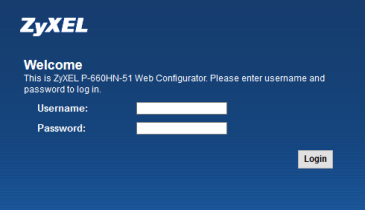
Enter the ZyXEL administrative credentials: username=admin & password=1234
Or, enter the ISP proprietary administrator credentials: must be obtained from the ISP
After the ZyXEL default credentials are entered a welcome screen will appear displaying information for the IP address that is accessing the web configuration screen and time being accessed. There will also be a number for failed login attempts from this IP. Uncheck the box for "Show this page next time" if you do not wish to see this info when you login to the WebGUI.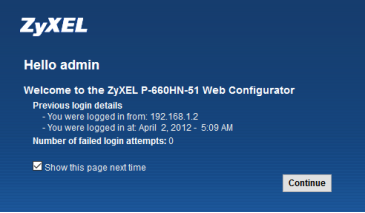
Wi-Fi Setup
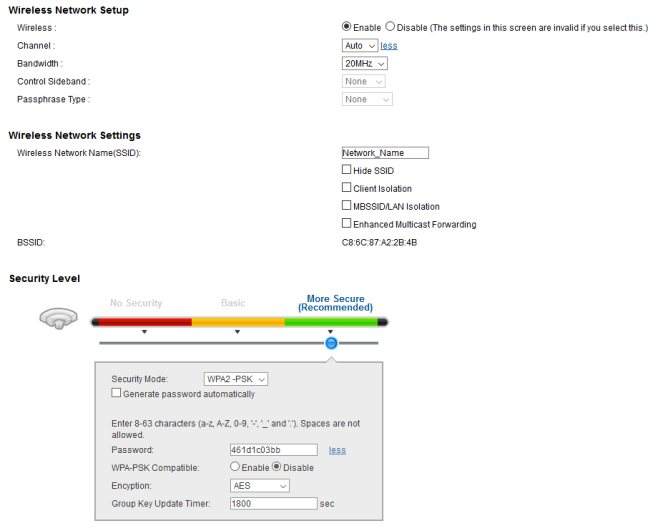
To setup a wireless network name (SSID), wireless security or make other changes to the wireless network mouse over the Network Setting menu option at the bottom of the screen. Select Wireless from the pop-up menu.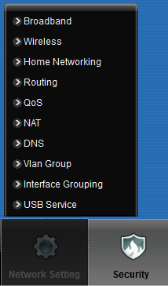
From the wireless menu you will see multiple tabs available (General, More AP, MAC Authentication, etc.). The General tab is where the wireless network name and wireless security can be configured.
- Wireless – Select the Enable or Disable radio to turn the wireless feature ON/OFF for the selected band.
- Channel – This refers to the channel the radio will use to broadcast the signal. An Auto option can be selected to allow the router to automatically choose the best channel to use based on its current environment, or, manually select the channel to use at all times.
- Bandwidth – Select the channel bonding width for the band.
- Control Sideband – This option is available when using 40MHz or higher bandwidth. Options are Upper and Lower, this depends the current channel the Wi-Fi is broadcasting on.
- Wireless Network Name (SSID) – The name of the wireless signal. It is recommended that this be changed to something more personal and unique.
- Hide SSID – Check the box to hide the network name. (Not recommended)
- Client Isolation – Isolates clients connected to the Wi-Fi so they cannot communicate with each other.
- MBSSID/LAN Isolation – Isolates clients on the LAN so they cannot communicate with WLAN clients.
- Multicast Forward – Select this option to convert wireless multicast traffic to wireless unicast traffic.
- Security Level – WPA2-PSK is the most secure method of encrypting wireless packets. It is recommended that "Generate Password Automatically" be disabled and a more secure password be created (by the user).
- Scroll down and click the Apply button to save the settings.
Wi-Fi Tweaks
The following are recommendations for optional wireless tweaks to provide better security and performance.
Disable Legacy 802.11 technology
If your wireless devices support 802.11n or better (802.11ac), it is highly recommended that older 802.11 technologies be disabled (802.11a/b/g). To use only newer 802.11n wireless, click on the Others tab and change the "802.11 Mode" to use 802.11n.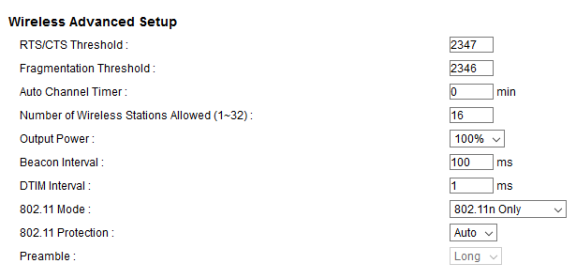
If you still have older devices using 802.11a/b/g which require a wireless connection, please do not change these settings.
Wireless Channel Selection
The wireless channel used to broadcast the signal can impact performance. There are high numbers of devices that create interference for the Wi-Fi signal and that number is growing. In urban areas wireless interference will be higher than rural areas. Other Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth devices, some cordless phones, microwave ovens and other sources can cause interference with your wireless signal. This interference may impact performance (speed/throughput) and signal coverage (distance). This problem is more noticeable on the 2.4Ghz spectrum. The 2.4Ghz wireless spectrum uses 11 possible channels in the US, mostly overlapping channels.
If is recommended that a site survey be executed in your environment to determine what the best channel to use will be. There are two ways to run a survey: hardware appliance or software on computer.
Hardware Appliance – Most hardware devices used for wireless site surveys can detect signals from Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and other sources. This is the best way to gather information on what signals are interfering in the environment. This is also pricey, hardware may start in the low hundred dollars and reach thousands.
Software Survey – This is a cheaper option as some companies offer free Wi-Fi site survey software. The only downside to this method is that only Wi-Fi signals cab be detected.
Channel Bandwidth (bonding)
Bonding channels will increase the throughput performance of your wireless connection. Bonding channels, however, can also increase wireless interference by overlapping channels. Example: Using a 40MHz channel bandwidth on the 2.4GHz spectrum, if the main broadcast channel is 11 and the route uses channel 7 for the bonding, the signal broadcast will receive interference from other devices using channels 3 and higher. Because of the low amount of possible non-overlapping channels on the 2.4GHz spectrum, it is recommended that channel bonding not be used, 20MHz bandwidth only.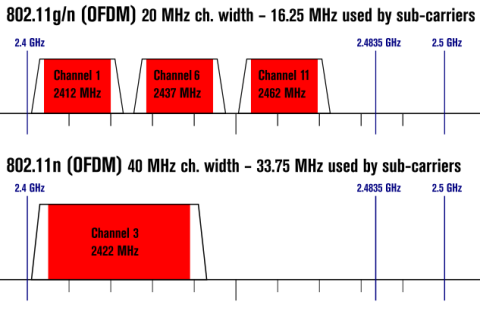
The 5GHz wireless spectrum uses more non-overlapping channels making better use of channel bonding with little to no interference.
WPA2 for Wireless Security
To maximize performance and security it is recommended that WPA2 encryption be used on the wireless network. WPA2 can use a password up to 63 characters in length; please keep in mind that the longer the password the more time it takes to encrypt/decrypt the packets over the wireless which may decrease performance. 802.11n/ac wireless standards require WPA2 encryption to reach HT (High Throughput) and/or VHT (Very High Throughput) data rates. Using a lower security method, WEP or WPA, will lower the 802.11 mode to use 802.11a/b/g.
Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
Developed in 2006 by the Wi-Fi Alliance to allow home users with little experience or knowledge about wireless security to add devices to the wireless network with encryption. There are four available methods to deploy WPS: WPS push button, PIN number, NFC (Near Field Communication) or USB flash drive.
It is recommended that the WPS feature be disabled due to design vulnerabilities. WPS requires an 8 digit PIN to authenticate client devices, this key may be cracked in about four hours or less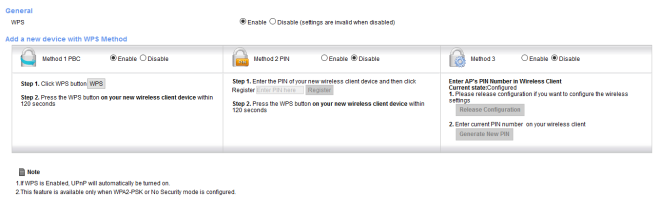
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.