Overview
NAT (Network Address Translation – RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP address of a host in a packet. NAT is used to make computers on a private network available to the outside world by using ports to forward packets to the appropriate private IP address.
Suppose you have two computers on your private network you want to use Remote Desktop to manage them from the outside world. Remote Desktop (RDP) works on port TCP:3389, because of the nature of NAT you can only forward the port one time to one computer.
So, if the RDP port (TCP:3389) can only be forwarded to one computer, how can we manage both computers from the outside world?
- One way to accomplish this would be to edit your computers registry to change the listening port, from TCP:3389 to something else. Editing the registry on your computer can cause problems if not done correctly, check the Microsoft knowledge base for instruction on how to change the RDP listening port on your version of Windows OS.
- The second option (and by far the easiest) would be to setup Port Translation on your router (if the feature is supported). For this guide we will go over the port translation option on the ZyWALL router(s) to accomplish this type of scenario.
Example: One NAT rule will be created normal, forwarding port 3389, untouched, to one of the servers. For the second NAT rule, traffic from outside will come in on port 3390 and the router will then modify the packet and push it to the second server on port 3389.
Supported Devices
ZyWALL 110 – running firmware version 3.10 and newer
ZyWALL 310 – running firmware version 3.10 and newer
ZyWALL 1100 – running firmware version 3.10 and newer
USG40 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG40W – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG60 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG60W – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG110 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG210 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG310 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG1100 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG1900 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
USG20-VPN – running firmware version 4.16 and newer
USG20W-VPN – running firmware version 4.16 and newer
USG2200-VPN – running firmware version 4.20 and newer
UAG2100 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
UAG4100 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
UAG5100 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
NXC2500 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
NXC5500 – running firmware version 4.10 and newer
Creating Objects
The ZLD series gateways are object based so objects for port numbers and device IP addresses will need to be created before you do anything else. Most routers allow you to type in the IP addresses and port numbers as you create your rules. The downside to this type of setup is re-configuring the router rules if IP addresses on the devices (computer, NAS, etc.) are changed or if the routers network IP scheme is changed. The user must go through all router menus where rules exist to change the IP setup. The advantage of having an object based router is that if you make a network change all you would need to do is update the object entry, instead of going through each individual menu and updating rules. Once the object is modified it updates all menus where the object is being utilized with the updated information.
Creating Service Object
You will need to create service objects for the port the traffic is coming in on and the port the server is listening to. Based on the example scenario above the traffic will be coming in over port 3390, the server (computer) is listening on port 3389. Port 3389 is a commonly used port so there is already a service object predefined on the appliance called “RDP” for this port. Port 3390 is a custom port; a service object will need to be added for this port. Go to Configuration → Object → Service and click the Add button to insert the new port object.
- Provide a name for the service object.
- Specify the protocol the port is using (TCP or UDP).
- Type in the start port number and end port number. (if service is for single port number you do not need to specify an end port, this is only needed for port ranges)
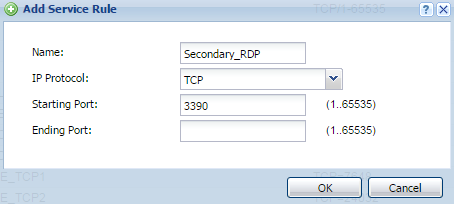
Repeat the process to add all your port (service) objects.
Creating Address Object
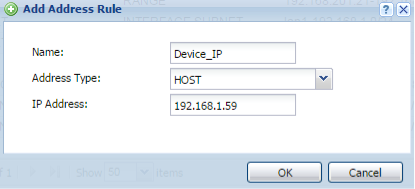
To create an object for the device IP address, go to Configuration → Object → Address. Click the Add button to insert the entry.
- Give the address object a name.
- Because the address object is for a single device IP address, make sure the “Address Type” is set for HOST.
- Provide the IP address of the device.
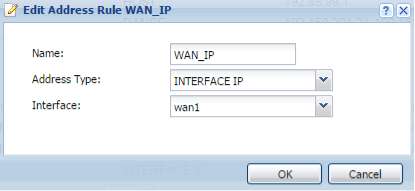
Create an additional address object for the WAN ports IP address.
- Give the address object a name.
- Set the “Address Type” for INTERFACE IP (this will allow the object to pull the address directly from the interface)
- Select the WAN port you want the object to pull the address from.
Repeat this process to add any other IP object entry for internal/external addresses.
Create Virtual Server Rule
To create the Virtual Server rule (port forwarding/translation), go to Network → NAT menu, and click the Add button.
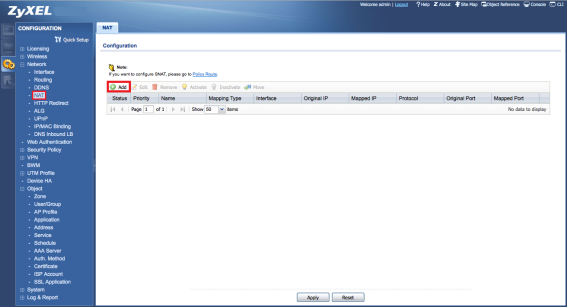
- Enable rule
- Insert a rule name
- Select Virtual Server
- Choose the incoming internet interface (usually WAN1 or GE1)
- Select the WAN_IP object as “Original IP”
- select Device_IP as “Mapped IP”
- Select Service for the “Port Mapping Type”
- In “Original Service” select the Secondary_RDP object for port 3390
- In “Mapped Service” select RDP object for port 3389
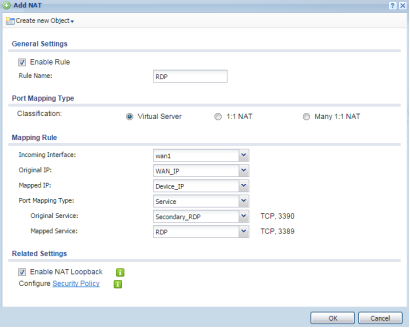
- Click the OK button
Note: NAT Loopback can be activated so internal clients can contact the server based on public info (WAN IP, DDNS hostname, Domain Name, etc.), only if Original IP is not set to ANY.
Create Policy Control Rule
As the final step, we need to create a Policy Control rule to allow traffic to pass through to the server. Go to the Security Policy → Policy Control menu and press the Add button to insert a rule.
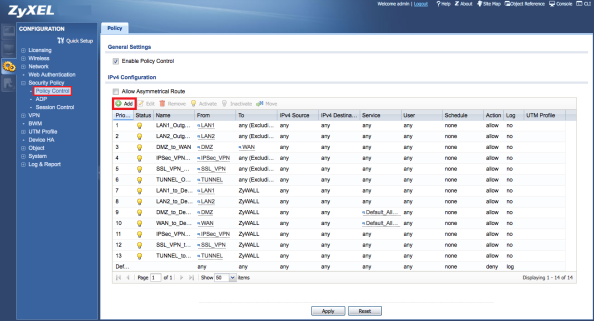
- Provide a name to the Policy Control rule.
- Select “FROM” WAN “TO” LAN1.
- Insert your servers IP-address object as Destination.
- Select your preferred Service or Service Group, in this case RDP is selected.
- Set “Access” as Allow.
- Enable “Log” if needed.
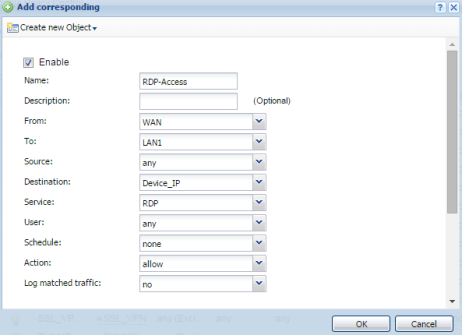
- Click the OK button
Testing and Troubleshooting
Attempt to open an RDP session using a device outside of the private network.
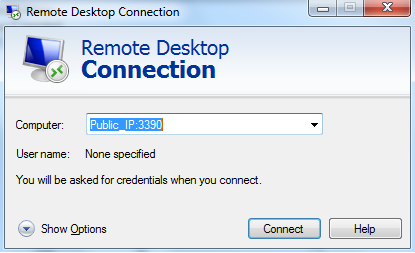
If the you receive an error from the client do the following.
- Disable the Firewall from the RDP server to make sure it is not blocking the RDP session access.
- Make sure the Remote Desktop feature is enabled on the computer.
- Disable the ZyXEL appliance policy control feature.
- Test the RDP session with a computer on the local network. If a computer on the same network cannot communicate with the RDP server using the private IP address and port 3389, there is something wrong with the server.
If RDP access works locally but still can’t get it to work from the internet please contact Tech Support for further assistance.
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.