This guide will provide instructions to manually configure the wireless setting on the Zyxel router as well as provide recommendation for best performance and results.
Overview
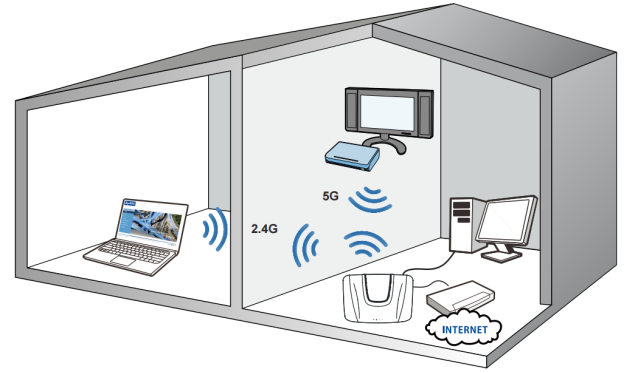
A wireless local area network (WLAN) allows communications between two or more devices using a wireless distribution system within a limited area such as a home, work office, etc. This technology allows devices capable of using IEEE 802.11 standards to communicate within a network or the internet. WLAN has become a popular technology to use to network computers and other devices because of its ease of installation and deployment. Wi-Fi provides a low cost solution to get all your devices connected to each other or the internet.
Supported Devices
ARMOR-Z1 (NBG6816)
Accessing the WebGUI
It is recommended that any configuration changes made to the router are done via a hardwired computer, especially when making changes to the wireless setup. Please be sure to have a computer connected to a LAN port (LAN1-LAN4) before proceeding with the setup changes. To access the web configuration screen for the ARMOR-Z1 (NBG6816) router, open an internet browser (Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, etc.). Type http://192.168.1.1 on the browsers address bar and press/hit the ENTER/RETURN key on your keyboard. This will open the routers login screen.
Type in the device password on the login screen to continue the setup. The default password for the Zyxel router is 1234. If the password was previously changed, type in the new password to continue.
Once logged in you will be prompted to change the administrative password, only if still using the default 1234 credentials. Type in a new password for the administrative credentials and click the Change button to save/apply the new setting, or, click the Skip button to continue into the web configuration screen and keep the administrative password as 1234.

Wireless LAN Menu
In the WebGUI click on the Expert option on the right side of the window, once in the expert mode click the Wireless menu option across the bottom of the window.

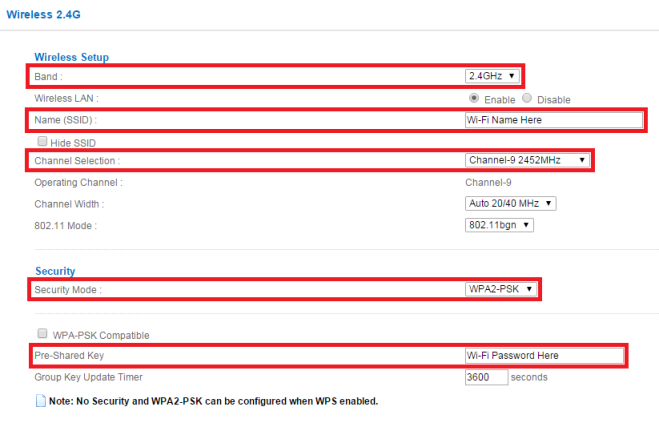
The Armor-Z1 (NBG6816) router is a dual band router, this means it can broadcast a wireless signal using a 2.4GHz wireless spectrum as well as the 5GHz wireless spectrum simultaneously. When clicking the Wireless menu option the 2.4GHz radio is preselected for configuration. Make the necessary changes to the 2.4GHz radio.
- Name (SSID) – Provide a name for the wireless signal. This is the name your wireless devices (clients) will see when scanning for Wi-Fi signals in the area.
- Channel Selection – By default this option is set to "Auto Channel Selection", this option will randomly scan the area for other wireless signals to select the best channel to work with. In th U.S. the allowed channels on the 2.4GHz spectrum are 1-11. The auto channel selection scans the area for interference on the different channels and selects the channel to use to best results based on channel interference, overlap, etc. Be aware that when the auto channel selection feature changes the channel to one with less interference all associated wireless clients will be dropped from the Wi-Fi while the change is applied. It is recommended that you manually specify which channel to broadcast the wireless signal, this will decrease the amount of dropped wireless signal occurrences due to auto channel selection feature making changes to the broadcast.
- Security Mode – This reflects the level of security or encryption to be used between the base station (router) and the wireless clients. It is recommended that the security mode be configured to use WPA2-PSK, this provides maximum security for wireless communications between router and clients. In order to take advantage of 802.11n wireless speeds it is also necessary to use WPA2-PSK, 802.11n does not support anything lower. Using a lower security mode will drop 802.11 mode to 802.11b/g speeds only (54Mbps max).
- Pre-Shared Key – Type in the password you wish to use to authenticate wireless clients.
- Click the Apply button on the top right portion of the window to save the settings.
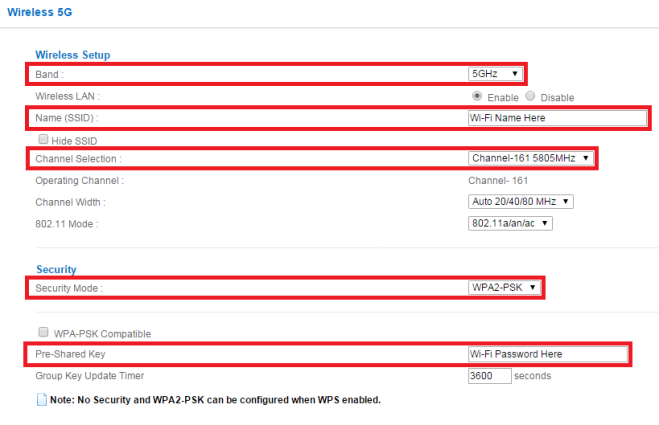
To configure the 5GHz radio click on the dropdown option for Band at the top of the menu and select the 5GHz radio option.
- Name (SSID) – Provide a name for the wireless signal. This is the name your wireless devices (clients) will see when scanning for Wi-Fi signals in the area.
- Channel Selection – By default this option is set to "Auto Channel Selection", this option will randomly scan the area for other wireless signals to select the best channel to work with. In th U.S. the allowed channels on the 5GHz spectrum supported by the router are 36, 40, 44, 48, 149, 153, 157 and 161. The auto channel selection scans the area for interference on the different channels and selects the channel to use to best results based on channel interference, overlap, etc. Be aware that when the auto channel selection feature changes the channel to one with less interference all associated wireless clients will be dropped from the Wi-Fi while the change is applied. It is recommended that you manually specify which channel to broadcast the wireless signal, this will decrease the amount of dropped wireless signal occurrences due to auto channel selection feature making changes to the broadcast.
- Security Mode – This reflects the level of security or encryption to be used between the base station (router) and the wireless clients. It is recommended that the security mode be configured to use WPA2-PSK, this provides maximum security for wireless communications between router and clients. In order to take advantage of 802.11n and/or 802.11ac wireless speeds it is also necessary to use WPA2-PSK, 802.11n and 802.11ac do not support anything lower. Using a lower security mode will drop 802.11 mode to 802.11a speeds only (54Mbps max).
- Pre-Shared Key – Type in the password you wish to use to authenticate wireless clients.
- Click the Apply button on the top right portion of the window to save the settings.
The Zyxel router is capable of wireless speeds up to 600Mbps on the 2.4GHz wireless spectrum using a 4x4 antenna configuration and 40MHz channel width, however, speeds will vary depending on hardware capabilities, distance from base station, obstacles and obstacle build materials as well as other variables.
The router is capable of wireless speeds up to 1733 Mbps on the 5GHz wireless spectrum using a 4x4 antenna configuration and just like the 2.4GHz radio, speeds will can vary based on network condition and environmental variables.
Troubleshooting
- Unable to establish a wireless connection?
- Disable wireless security
- Change the SSID to rule out special characters being the problem.
- Make sure firmware on router is up to date.
- Try different wireless channels to make sure it is not wireless interference causing the problem.
- Make sure the wireless card drivers are up to date. (This would involve the user checking the computer manufacturer's website or the wireless card chipset manufacturers website for updates)
- Change the 802.11 mode. (Legacy wireless cards may have a hard time connecting to a wireless network using 40MHz channel bandwidth used by 802.11n/ac)
- Slow wireless speeds? Multiple variables can cause a slow connection.
- Check what 802.11 technology the client computer is using on the connection link.
802.11a – speeds up to 54Mbps
802.11b – speeds up to 11Mbps
802.11g – speeds up to 54Mbps or 108Mbps using MIMO (multiple-input, multiple-output)
802.11n – speeds up to 600Mbps*
802.11ac – speeds up to 6933.3Mbps*
Note: 802.11n has a feature that cuts the link speed in half if there is another 802.11n broadcast in the area. So a router that supports an 802.11n connection up to 300Mbps will be cut in half to 150Mbps.
*depending on spatial streams (antenna array) - Check the speed at different distances, this will always be a factor. Also, if using wireless technology with 40MHz bandwidth and higher, speeds will be fast at close range but wider channel bandwidth will be greatly impacted at farther distances. (802.11ac uses Beamforming to help maintain high speeds at great distances)
- How is the speed being tested? The size of the packets used, protocol type, hardware and/or software can impact results. If the test is being run/ran against an online server, verify the internet speeds from the ISP by bypassing all networking equipment and connecting directly to the ISP modem.
- Are speeds identical across all devices?
- How many clients are connected to the Wi-Fi? We do not recommend connecting more than 12 wireless clients on residential access points. The wireless connection throughput is shared among all connected devices, the more devices connected the lower the throughput.
- Try different wireless channels to rule out wireless interference causing the problem.
- Wireless signal output range is low? Multiple variables can cause a low signal output.
- Building materials – the denser the material the more it obstructs the signals flow.
- Antenna gain and Wireless radio output power will impact the distance the signal can cover. The higher the gain of the antenna the greater distance that can be covered, but you cannot place a higher gain antenna than what the wireless radio can support. If the antenna gain is too high the wireless radio may not be able to supply sufficient power. Changing the antennas can improve signal output, if antennas are external and removable.
- Position of the antennas – depending on the antenna (whether Omni-directional or directional) can impact the signal if pointing the wrong way. Wireless routers and access points with internal antenna don't really suffer from this.
- Wireless Interference – the greater the interference from neighboring Wi-Fi access points or other equipment overlapping the 2.4GHz spectrum the lower the signal output. Change wireless channels or do a survey (wireless survey) of your environment to see what channel has the least interference for use.
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.